 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
|||
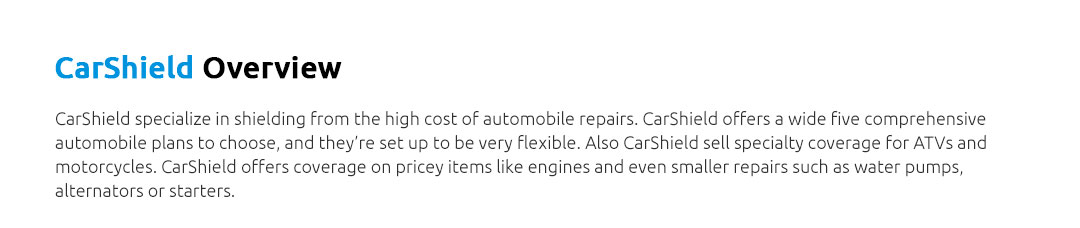 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|

Exploring Motor Vehicle Warranty Plans: A Comprehensive GuideIn today's fast-paced world, where vehicles are an integral part of daily life, the importance of a reliable warranty plan cannot be overstated. As one embarks on the journey of understanding motor vehicle warranty plans, it becomes clear that the landscape is vast and varied, with each option presenting its own set of advantages and potential drawbacks. The primary purpose of a warranty plan is to offer peace of mind to the vehicle owner, safeguarding against unexpected repairs and associated costs. However, with a plethora of choices available, selecting the most suitable plan requires careful consideration and a nuanced understanding of the options at hand. Broadly speaking, motor vehicle warranty plans can be categorized into two main types: manufacturer warranties and third-party warranties. Manufacturer warranties, often considered the gold standard, are typically included with the purchase of a new vehicle. These warranties generally cover a specified period or mileage, such as three years or 36,000 miles, whichever comes first. Their primary advantage lies in their comprehensive nature, often covering repairs and replacements for a wide range of vehicle components. On the other hand, third-party warranties, sometimes referred to as extended service contracts, offer an appealing alternative, particularly for used car owners or those seeking additional coverage beyond the manufacturer's warranty. These plans can be tailored to suit individual needs, with options ranging from basic powertrain coverage to more extensive plans that include components such as air conditioning and electrical systems. One of the notable benefits of third-party warranties is their flexibility; however, it is crucial to thoroughly vet the provider to ensure reliability and customer satisfaction. When comparing these options, several factors come into play.
https://www.reddit.com/r/MechanicAdvice/comments/1fppzet/is_there_an_extended_car_warranty_company_that_is/
There is an aftermarket extended warranty company I see frequently that is good about coverage, I'll have to ask when I get in today what the ... https://olive.com/coverage-plans/
Cylinder Heads ; Diesel Injector Pump ; Engine Mounts ; Engine Seals and Gaskets. https://www.berkshirehathawayautomotive.com/mpp/warranty-plans.htm
Manufacturer's Warranties are limited. So to make sure you're covered, consider one of three levels of protection with an MPP Extended Service Contract for ...
|